

Table of Contents
Shirovirechana: An Introduction
The concept of “Nose to Brain Drop” refers to the delivery of medicines through the nasal route directly into the brain. This method bypasses the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and provides a fast and efficient means of targeting the central nervous system. Both modern medical science and Ayurveda acknowledge its therapeutic potential and have applied it in various neurological and psychological conditions.
Anatomical and Physiological Basis
The nose and brain are closely connected through two primary pathways:
Olfactory Nerve Pathway: Medications reach the brain via the olfactory epithelium located at the upper part of the nasal cavity, passing through the olfactory bulb into the brain.
Trigeminal Nerve Pathway: Some drugs utilize the trigeminal nerve to access specific regions of the brain.
These paths offer a unique advantage in delivering molecules that cannot cross the BBB when administered orally or intravenously.
Applications in Modern Medicine
The nose-to-brain route is being explored and utilized in various conditions such as:
Neurodegenerative Disorders: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Multiple sclerosis
Psychiatric Conditions: Anxiety, Depression, Schizophrenia
Pain Management: Migraine, Cluster headaches
Vaccines & Peptides: Research includes nasal vaccines and peptide-based therapies like intranasal insulin for cognitive enhancement.
Benefits include:
Avoidance of liver metabolism (first-pass effect)
High bioavailability
Rapid onset of action
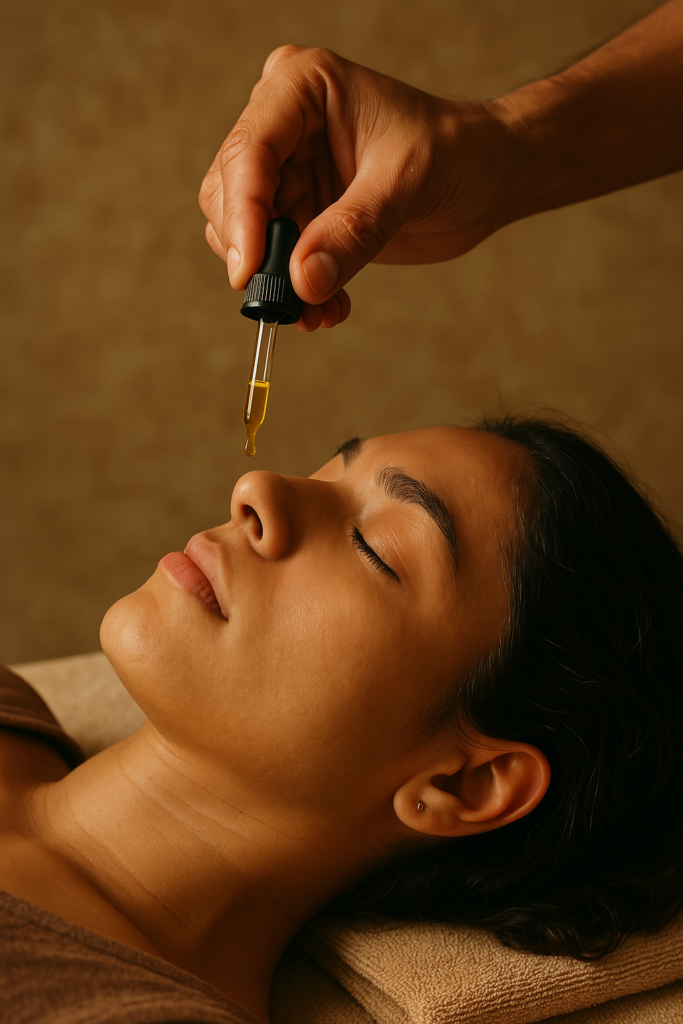
Nose to Brain in Ayurveda: The Concept of Nasya
https://drbuddhipaudel.com.np/blogs/happy-hormones/In Ayurveda, this technique is known as Nasya Karma, one of the five primary detoxification procedures in Panchakarma.
Purpose of Nasya:
Purification and nourishment of organs above the clavicle (brain, eyes, nose, ears, etc.)
Enhancing memory, concentration, and mental clarity
Managing diseases of the head and nervous system
Types of Nasya:
Virechana Nasya: Cleansing type
Brimhana Nasya: Nourishing type
Shamana Nasya: Pacifying type
Navana Nasya: Medicated oils and juices
Marsha Nasya: Full therapeutic dose
Pratimarsha Nasya: Daily minimal dose (safe for regular use)
Common Medications:
Anu Taila
Shadbindu Taila
Brahmi Ghrita
Jyotishmati Taila
Ksheerabala Taila
Scientific Basis
Bypassing the BBB: Nose-to-brain delivery avoids the restrictive blood-brain barrier.
Rapid Brain Access: Immediate access to the brain makes it ideal for neurological emergencies.
High Absorption: The nasal mucosa offers a highly vascularized surface for quick absorption.
Minimal Systemic Side Effects: As the drug is targeted, systemic exposure is limited.
Safety, Precautions, and Contraindications:
Precautions:
Proper posture (reclining with the head tilted backward)
Clean nasal passages
Use under expert supervision
When to Avoid:
Acute rhinitis or nasal infections
Nasal blockages
Children below 5 and elderly above 70 (with caution)
Conclusion:
The “Nose to Brain Drop” is a powerful and promising technique, harmonizing modern pharmacology with ancient Ayurvedic wisdom. It provides a direct, effective, and safe route to address a wide range of neurological, psychological, and systemic health concerns. When used correctly, this method can revolutionize drug delivery systems and preventive healthcare.
Shirovirechana Shirovirechana Shirovirechana Shirovirechana Shirovirechana Shirovirechana


10oxqv
8p7v4n
zo54ae